1. JWT란 무엇인지 알아봅니다.
2. JWT와 쿠키(Cookie), 세션(Session)의 차이점을 이해합니다.
3. jsonwebtoken 라이브러리를 이용해 JWT를 Express.js에서 사용해봅니다.
01. JWT란?
1) JWT(Json Web Token)
JWT(Json Web Token)은 웹 표준으로써, 서버와 클라이언트 사이에서 정보를 안전하게 전송하기 위해 도움을 주는 웹 토큰(Web Token)입니다.
JSON 형태의 데이터를 안전하게 전송하고 검증할 수 있는 기능을 제공합니다.
인터넷 표준으로서 자리잡은 규격입니다.
다양한 암호화 알고리즘을 사용할 수 있어, 신뢰성을 보장합니다.
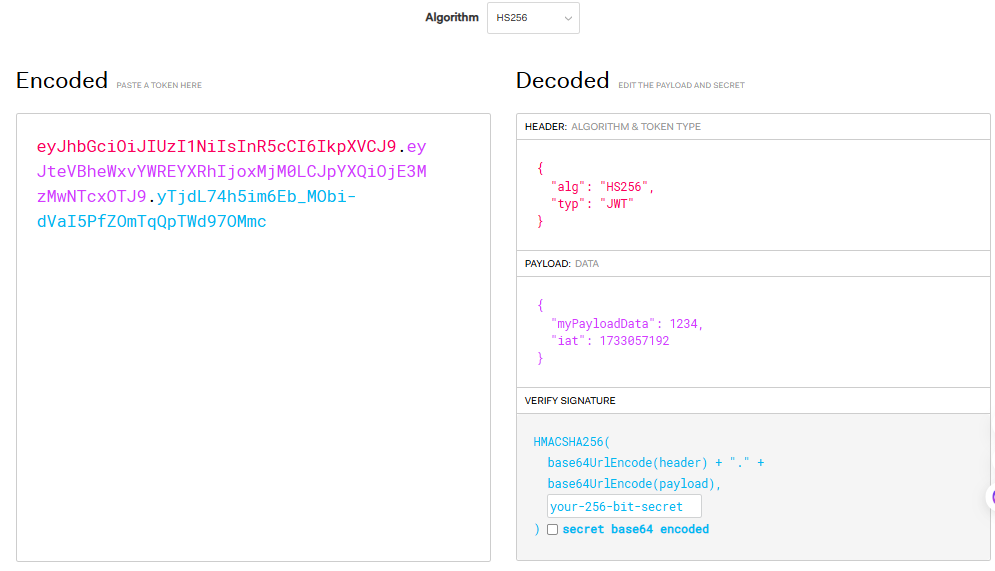
header.payload.signature 의 형식으로 3가지의 데이터를 포함합니다. (개미처럼 머리, 가슴, 배)
→ 때문에, JWT 형식으로 변환 된 데이터는 항상 2개의 '.' 이 포함된 데이터여야 합니다.
구성

jwt - Header, Payload, Signature
JWT(Json Web Token)는 크게 세 부분, 헤더(Header), 페이로드(Payload), 서명(Signature)로 구성되어 있습니다. 각각의 부분은 점(.)으로 분리됩니다.
JWT의 구조는 https://jwt.io/ 에서 간단히 확인할 수 있는데요, 위에서 말했듯이 개미처럼 머리, 가슴, 배와 같은 3가지를 가졌습니다.
Header(머리): 헤더는 토큰의 타입과 어떤 암호화를 사용하여 생성된 데이터인지 정의되어 있습니다.
alg : 암호화 방법
typ : 토큰 타입. jwt 토큰이 맞는지 확인 할 수 있습니다.
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
Payload(가슴): 페이로드는 실제 전달하려는 데이터를 담고 있습니다. 대표적으로 개발자가 원하는 데이터를 저장합니다.
sub, name : 실제로 전달하려는 데이터
iat : 유효기한입니다.
{
"sub": "1234567890",
"name": "John Doe",
"iat": 1516239022
}
Signature(배): 서명은 헤더와 페이로드, 그리고 비밀 키(Secret Key)를 이용하여 생성됩니다. 이 서명은 토큰이 변조되지 않은 정상적인 토큰인지 확인할 수 있게 도와줍니다. 변조방지
HMACSHA256(
base64UrlEncode(header) + "." +
base64UrlEncode(payload),
secret
)
각 부분을 Base64로 인코딩하여, 점(.) 으로 연결하면 최종적으로 JWT를 생성하게 됩니다. 이렇게 생성된 JWT는 이전에 배운 쿠키(Cookie) 또는 Path Parameter를 통해 전달될 수 있습니다.
JWT의 특성 정리하기
변조방지기능만 있는 셈. 누구나 데이터를 확인 간능함.
1. JWT는 비밀 키를 모르더라도 복호화(Decode)가 가능합니다.
- JWT를 가진 사람이라면 누구나 해당 토큰에 어떤 데이터가 담겨있는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 변조만 불가능 할 뿐, 누구나 복호화하여 보는것은 가능하다는 의미가 됩니다!
2 . 민감한 정보(개인정보, 비밀번호 등)는 담지 않도록 해야합니다.
- JWT의 페이로드는 누구나 복호화하여 볼 수 있기 때문입니다.
3 . JavaScript와 같이 특정 언어에서만 사용 가능한것은 아닙니다
- JWT는 단순히 데이터 형식일 뿐, 단지 개념으로서 존재하고, 이 개념을 코드로 구현하여 공개된 코드를 우리가 사용하는게 일반적입니다.
4) JWT는 쿠키, 세션과 어떻게 다른가요?
데이터를 교환하고 관리하는 방식인 쿠키/세션과 달리, JWT는 단순히 데이터를 표현하는 형식입니다.
JWT로 만든 데이터는 변조가 어렵고, 서버에 별도의 상태 정보를 저장하지 않기 때문에, 서버를 Stateless(무상태)로 관리할 수 있습니다.
쿠키와 세션은 사용자의 로그인 정보나 세션 데이터를 서버에 저장하므로 상태를 유지합니다. 때문에, Stateful(상태 보존)하게 데이터가 관리됩니다.
Stateless(무상태)와 Stateful(상태 보존)의 차이를 간단히 설명하자면,
Node.js 서버가 언제든 죽었다 살아나도 똑같은 동작을 하면 Stateless하다고 볼 수 있습니다.
반대로 서버가 죽었다 살아났을때 조금이라도 동작이 다른 경우 Stateful하다고 볼 수 있겠죠.
서버가 스스로 어떤 기억을 갖고 다른 결정을 하냐 마냐의 차이라고 보면 더 쉽습니다
로그인 정보를 서버에 저장하게 되면 무조건 Stateful(상태 보존)이라고 볼 수 있습니다.
02. JWT는 어떻게 사용하면 되나요?
1) 오픈소스 라이브러리를 이용합니다.
jsonwebtoken 라이브러리는 Node.js에서 제일 사용량이 많은 라이브러리입니다.
프로젝트로 이용할 폴더를 생성하고, 해당 경로에서 명령어로 우리가 필요한 모듈을 설치합니다
# yarn을 이용해 프로젝트를 초기화합니다.
yarn init -y
# jsonwebtoken, express 라이브러리를 설치합니다.
yarn add jsonwebtoken expressyarn을 이용해 생성된 package.json 파일에서 type을 module로 꼭 변경해야 합니다.
이 설정은 프로젝트에서 ES6 모듈(import/export)을 사용할 수 있도록 설정해줍니다
2) 우리가 원하는 JSON 데이터를 암호화합니다.
데이터를 암호화 하기
jsonwebtoken 라이브러리의 sign 메서드를 사용해 JWT를 생성합니다.
// app.js
import jwt from 'jsonwebtoken';
const token = jwt.sign({ myPayloadData: 1234 }, 'mysecretkey');
console.log(token); // eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJteVBheWxvYWREYXRhIjoxMjM0LCJpYXQiOjE2OTA4NzM4ODV9.YUmYY9aef9HOO8f2d6Umh2gtWRXJjDkzjm5FPhsQEA0
데이터는 Payload에 담깁니다. jwt.io 에서인코딩 된 데이터를 복호화하세요
{
"myPayloadData": 1234,
"iat": 1733057192
}
sign 메서드는 첫 번째 인자로 Payload 데이터를, 두 번째 인자로 비밀 키를 받아 JWT를 생성합니다
→ 여기서, Payload는 문자열 뿐만 아니라, 객체도 할당할 수 있습니다.
3) 복호화를 해봅니다!
jsonwebtoken 라이브러리의 decode 메서드를 사용해 JWT를 복호화합니다.
//app.js
import jwt from 'jsonwebtoken';
const token = "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJteVBheWxvYWREYXRhIjoxMjM0LCJpYXQiOjE2OTA4NzM4ODV9.YUmYY9aef9HOO8f2d6Umh2gtWRXJjDkzjm5FPhsQEA0";
const decodedValue = jwt.decode(token);
console.log(decodedValue); // { myPayloadData: 1234, iat: 1690873885 }
JWT는 누구나 복호화가 가능합니다. 그저 검증을 통해 변조가 되지 않은 데이터인지 확인할 수 있습니다.
복호화된 JWT를 출력합니다
복호화가 아닌, 변조되지 않은 데이터인지 검증해봅시다
jsonwebtoken 라이브러리의 verify 메서드를 사용해 JWT를 검증합니다.
// app.js
import jwt from 'jsonwebtoken';
const token = "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJteVBheWxvYWREYXRhIjoxMjM0LCJpYXQiOjE2OTA4NzM4ODV9.YUmYY9aef9HOO8f2d6Umh2gtWRXJjDkzjm5FPhsQEA0";
// 변조 검증(어떤 비밀키로 만들어졌는지 검증)
// jwt.verify(token, "비밀키이름")
const decodedValueByVerify = jwt.verify(token, "mysecretkey");
console.log(decodedValueByVerify); // { myPayloadData: 1234, iat: 1690873885 }
검증에 실패하면 에러가 발생하게됩니다.
잘못된 비밀키를 입력해서 데이터를 검증해봅시다.
잘못된 비밀 키를 이용해 JWT를 검증하면, 에러가 발생합니다.
//app.js
import jwt from 'jsonwebtoken';
const token = "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJteVBheWxvYWREYXRhIjoxMjM0LCJpYXQiOjE2OTA4NzM4ODV9.YUmYY9aef9HOO8f2d6Umh2gtWRXJjDkzjm5FPhsQEA0";
const decodedValueByVerify = jwt.verify(token, "secretkey");
console.log(decodedValueByVerify);
// JsonWebTokenError: invalid signature
//app.js
import jwt from "jsonwebtoken";
// Encoded
const token = jwt.sign({ myPayloadData: 1234 }, "mysecretkey");
console.log("token : ", token); // eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJteVBheWxvYWREYXRhIjoxMjM0LCJpYXQiOjE2OTA4NzM4ODV9.YUmYY9aef9HOO8f2d6Umh2gtWRXJjDkzjm5FPhsQEA0
// Decoded
const decodedValue = jwt.decode(token);
console.log("decoded : ", decodedValue); // { myPayloadData: 1234, iat: 1690873885 }
// Modulation verification
const decodedValueByVerify = jwt.verify(token, "mysecretkey");
console.log("변조확인 : ", decodedValueByVerify); // { myPayloadData: 1234, iat: 1690873885 }
const wrongVerify = jwt.verify(token, "secretkey");
console.log("잘못된 키 변조확인 : ", wrongVerify);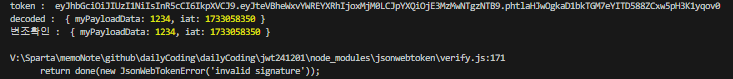
4) JWT를 사용하는 이유
JWT는 두 가지 중요한 특징을 가지고 있습니다.
1. JWT가 인증 서버에서 발급되었는지 위변조 여부를 확인할 수 있습니다.
2. 누구든지 JWT 내부에 들어있는 정보를 확인할 수 있습니다. (복호화)
만약 JWT를 사용하지 않은 상태에서 사용자 로그인을 구현하려고 하면 어떻게 될까요?
JWT를 적용하지 않은 로그인 API를 만들어봅시다
// app.js
import express from 'express';
const app = express();
app.post('/login', function (req, res, next) {
const user = { // 사용자 정보
userId: 203, // 사용자의 고유 아이디 (Primary key)
email: "archepro84@gmail.com", // 사용자의 이메일
name: "이용우", // 사용자의 이름
}
res.cookie('sparta', user); // sparta 라는 이름을 가진 쿠키에 user 객체를 할당합니다.
return res.status(200).end();
});
app.listen(5002, () => {
console.log(5002, "번호로 서버가 켜졌어요!");
});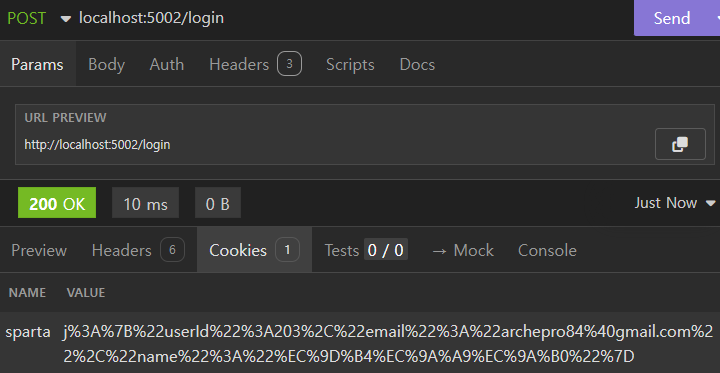
아무런 정보 없이 쿠키만 전달해줍니다.
사용자의 정보가 sparta 이름을 가진 쿠키에 할당됩니다.
쿠키의 속성값이나 만료 시간을 클라이언트가 언제든지 수정할 수 있습니다.
쿠키의 위변조 여부를 확인 할 수 없습니다.
JWT를 적용한 로그인 API는 어떻게 다를까요?
// app.js
import express from 'express';
import JWT from 'jsonwebtoken';
const app = express();
app.post('/login', (req, res) => {
// 사용자 정보
const user = {
userId: 203,
email: 'archepro84@gmail.com',
name: '이용우',
};
// 사용자 정보를 JWT로 생성
const userJWT = JWT.sign(
user, // user 변수의 데이터를 payload에 할당
'secretOrPrivateKey', // JWT의 비밀키를 secretOrPrivateKey라는 문자열로 할당
{ expiresIn: '1h' }, // JWT의 인증 만료시간을 1시간으로 설정
);
// userJWT 변수를 sparta 라는 이름을 가진 쿠키에 Bearer 토큰 형식으로 할당
res.cookie('sparta', `Bearer ${userJWT}`);
return res.status(200).end();
});
app.listen(5002, () => {
console.log(5002, '번호로 서버가 켜졌어요!');
});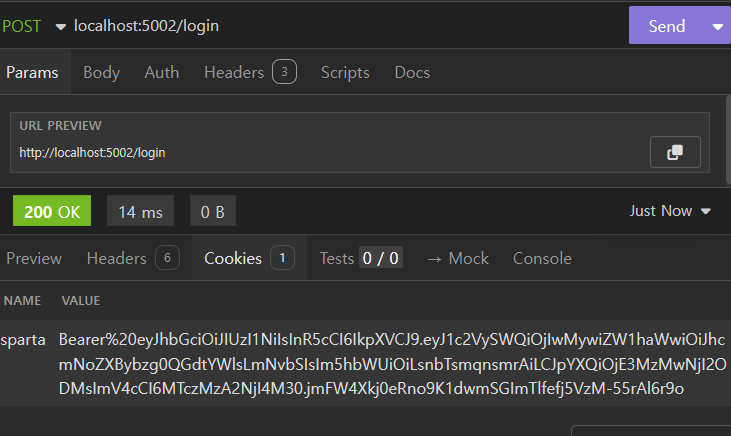
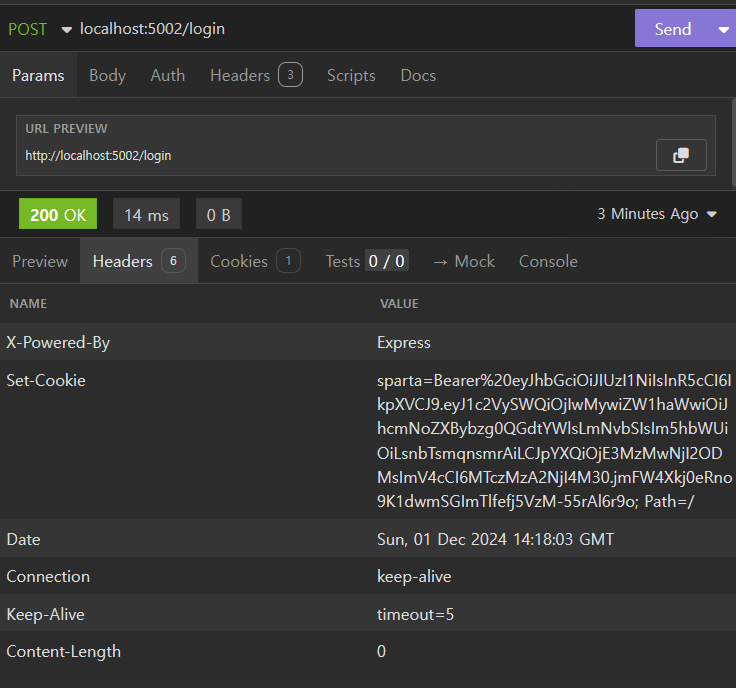
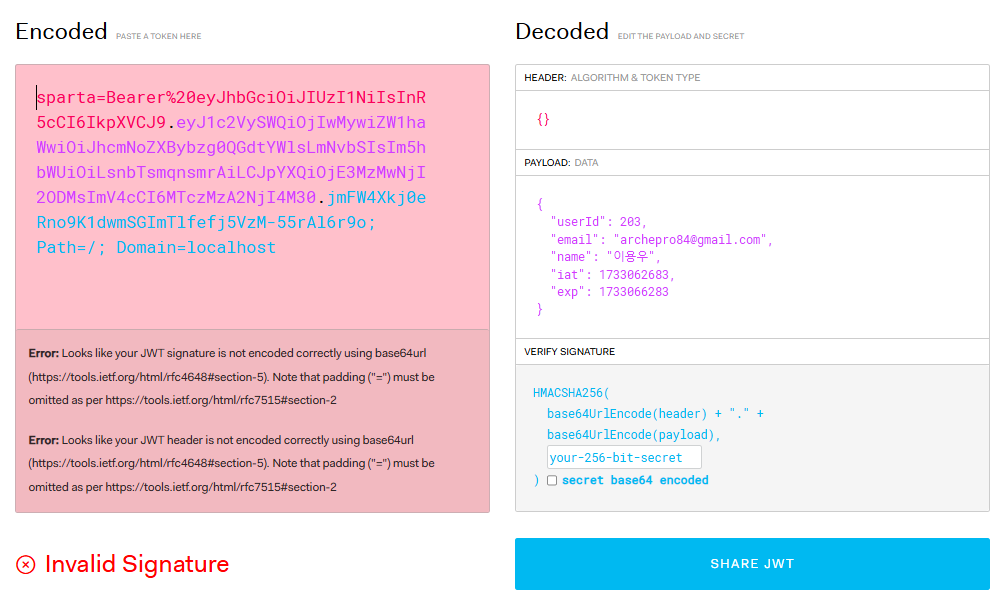
사용자의 정보를 Payload에 저장한 JWT를 sparta 이름을 가진 쿠키에 할당됩니다.
JWT를 생성할 때 위변조 여부를 확인할 수 있는 비밀키를 사용하였습니다.
쿠키의 만료시간과 별개로 JWT의 만료시간을 설정하였습니다.
다양한 JWT 옵션 보기
Ctrl + 'JWT.sign 클릭
// C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Microsoft\TypeScript\5.6\node_modules\@types\jsonwebtoken\index.d.ts
/// <reference types="node" />
import type { createPrivateKey, createPublicKey, KeyObject } from "crypto";
export class JsonWebTokenError extends Error {
inner: Error;
constructor(message: string, error?: Error);
}
export class TokenExpiredError extends JsonWebTokenError {
expiredAt: Date;
constructor(message: string, expiredAt: Date);
}
/**
* Thrown if current time is before the nbf claim.
*/
export class NotBeforeError extends JsonWebTokenError {
date: Date;
constructor(message: string, date: Date);
}
export interface SignOptions {
/**
* Signature algorithm. Could be one of these values :
* - HS256: HMAC using SHA-256 hash algorithm (default)
* - HS384: HMAC using SHA-384 hash algorithm
* - HS512: HMAC using SHA-512 hash algorithm
* - RS256: RSASSA using SHA-256 hash algorithm
* - RS384: RSASSA using SHA-384 hash algorithm
* - RS512: RSASSA using SHA-512 hash algorithm
* - ES256: ECDSA using P-256 curve and SHA-256 hash algorithm
* - ES384: ECDSA using P-384 curve and SHA-384 hash algorithm
* - ES512: ECDSA using P-521 curve and SHA-512 hash algorithm
* - none: No digital signature or MAC value included
*/
algorithm?: Algorithm | undefined;
keyid?: string | undefined;
/** expressed in seconds or a string describing a time span [zeit/ms](https://github.com/zeit/ms.js). Eg: 60, "2 days", "10h", "7d" */
expiresIn?: string | number;
/** expressed in seconds or a string describing a time span [zeit/ms](https://github.com/zeit/ms.js). Eg: 60, "2 days", "10h", "7d" */
notBefore?: string | number | undefined;
audience?: string | string[] | undefined;
subject?: string | undefined;
issuer?: string | undefined;
jwtid?: string | undefined;
mutatePayload?: boolean | undefined;
noTimestamp?: boolean | undefined;
header?: JwtHeader | undefined;
encoding?: string | undefined;
allowInsecureKeySizes?: boolean | undefined;
allowInvalidAsymmetricKeyTypes?: boolean | undefined;
}
export interface VerifyOptions {
algorithms?: Algorithm[] | undefined;
audience?: string | RegExp | Array<string | RegExp> | undefined;
clockTimestamp?: number | undefined;
clockTolerance?: number | undefined;
/** return an object with the decoded `{ payload, header, signature }` instead of only the usual content of the payload. */
complete?: boolean | undefined;
issuer?: string | string[] | undefined;
ignoreExpiration?: boolean | undefined;
ignoreNotBefore?: boolean | undefined;
jwtid?: string | undefined;
/**
* If you want to check `nonce` claim, provide a string value here.
* It is used on Open ID for the ID Tokens. ([Open ID implementation notes](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#NonceNotes))
*/
nonce?: string | undefined;
subject?: string | undefined;
maxAge?: string | number | undefined;
allowInvalidAsymmetricKeyTypes?: boolean | undefined;
}
export interface DecodeOptions {
complete?: boolean | undefined;
json?: boolean | undefined;
}
export type VerifyErrors =
| JsonWebTokenError
| NotBeforeError
| TokenExpiredError;
export type VerifyCallback<T = Jwt | JwtPayload | string> = (
error: VerifyErrors | null,
decoded: T | undefined,
) => void;
export type SignCallback = (
error: Error | null,
encoded: string | undefined,
) => void;
// standard names https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc7515.html#section-4.1
export interface JwtHeader {
alg: string | Algorithm;
typ?: string | undefined;
cty?: string | undefined;
crit?: Array<string | Exclude<keyof JwtHeader, "crit">> | undefined;
kid?: string | undefined;
jku?: string | undefined;
x5u?: string | string[] | undefined;
"x5t#S256"?: string | undefined;
x5t?: string | undefined;
x5c?: string | string[] | undefined;
}
// standard claims https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7519#section-4.1
export interface JwtPayload {
[key: string]: any;
iss?: string | undefined;
sub?: string | undefined;
aud?: string | string[] | undefined;
exp?: number | undefined;
nbf?: number | undefined;
iat?: number | undefined;
jti?: string | undefined;
}
export interface Jwt {
header: JwtHeader;
payload: JwtPayload | string;
signature: string;
}
// https://github.com/auth0/node-jsonwebtoken#algorithms-supported
export type Algorithm =
| "HS256"
| "HS384"
| "HS512"
| "RS256"
| "RS384"
| "RS512"
| "ES256"
| "ES384"
| "ES512"
| "PS256"
| "PS384"
| "PS512"
| "none";
export type SigningKeyCallback = (
error: Error | null,
signingKey?: Secret | PublicKey,
) => void;
export type GetPublicKeyOrSecret = (
header: JwtHeader,
callback: SigningKeyCallback,
) => void;
export type PublicKey = Parameters<typeof createPublicKey>[0];
export type PrivateKey = Parameters<typeof createPrivateKey>[0];
export type Secret =
| string
| Buffer
| KeyObject
| { key: string | Buffer; passphrase: string };
/**
* Synchronously sign the given payload into a JSON Web Token string
* payload - Payload to sign, could be an literal, buffer or string
* secretOrPrivateKey - Either the secret for HMAC algorithms, or the PEM encoded private key for RSA and ECDSA.
* [options] - Options for the signature
* returns - The JSON Web Token string
*/
export function sign(
payload: string | Buffer | object,
secretOrPrivateKey: Secret | PrivateKey,
options?: SignOptions,
): string;
export function sign(
payload: string | Buffer | object,
secretOrPrivateKey: null,
options?: SignOptions & { algorithm: "none" },
): string;
/**
* Sign the given payload into a JSON Web Token string
* payload - Payload to sign, could be an literal, buffer or string
* secretOrPrivateKey - Either the secret for HMAC algorithms, or the PEM encoded private key for RSA and ECDSA.
* [options] - Options for the signature
* callback - Callback to get the encoded token on
*/
export function sign(
payload: string | Buffer | object,
secretOrPrivateKey: Secret | PrivateKey,
callback: SignCallback,
): void;
export function sign(
payload: string | Buffer | object,
secretOrPrivateKey: Secret | PrivateKey,
options: SignOptions,
callback: SignCallback,
): void;
export function sign(
payload: string | Buffer | object,
secretOrPrivateKey: null,
options: SignOptions & { algorithm: "none" },
callback: SignCallback,
): void;
/**
* Synchronously verify given token using a secret or a public key to get a decoded token
* token - JWT string to verify
* secretOrPublicKey - Either the secret for HMAC algorithms, or the PEM encoded public key for RSA and ECDSA.
* [options] - Options for the verification
* returns - The decoded token.
*/
export function verify(
token: string,
secretOrPublicKey: Secret | PublicKey,
options: VerifyOptions & { complete: true },
): Jwt;
export function verify(
token: string,
secretOrPublicKey: Secret | PublicKey,
options?: VerifyOptions & { complete?: false },
): JwtPayload | string;
export function verify(
token: string,
secretOrPublicKey: Secret | PublicKey,
options?: VerifyOptions,
): Jwt | JwtPayload | string;
/**
* Asynchronously verify given token using a secret or a public key to get a decoded token
* token - JWT string to verify
* secretOrPublicKey - A string or buffer containing either the secret for HMAC algorithms,
* or the PEM encoded public key for RSA and ECDSA. If jwt.verify is called asynchronous,
* secretOrPublicKey can be a function that should fetch the secret or public key
* [options] - Options for the verification
* callback - Callback to get the decoded token on
*/
export function verify(
token: string,
secretOrPublicKey: Secret | PublicKey | GetPublicKeyOrSecret,
callback?: VerifyCallback<JwtPayload | string>,
): void;
export function verify(
token: string,
secretOrPublicKey: Secret | PublicKey | GetPublicKeyOrSecret,
options: VerifyOptions & { complete: true },
callback?: VerifyCallback<Jwt>,
): void;
export function verify(
token: string,
secretOrPublicKey: Secret | PublicKey | GetPublicKeyOrSecret,
options?: VerifyOptions & { complete?: false },
callback?: VerifyCallback<JwtPayload | string>,
): void;
export function verify(
token: string,
secretOrPublicKey: Secret | PublicKey | GetPublicKeyOrSecret,
options?: VerifyOptions,
callback?: VerifyCallback,
): void;
/**
* Returns the decoded payload without verifying if the signature is valid.
* token - JWT string to decode
* [options] - Options for decoding
* returns - The decoded Token
*/
export function decode(token: string, options: DecodeOptions & { complete: true }): null | Jwt;
export function decode(token: string, options: DecodeOptions & { json: true }): null | JwtPayload;
export function decode(token: string, options?: DecodeOptions): null | JwtPayload | string;
유효기한 설정
expiresIn:
// expiresIn:
ms('2 days') // 172800000
ms('1d') // 86400000
ms('10h') // 36000000
ms('2.5 hrs') // 9000000
ms('2h') // 7200000
ms('1m') // 60000
ms('5s') // 5000
ms('1y') // 31557600000
ms('100') // 100
ms('-3 days') // -259200000
ms('-1h') // -3600000
ms('-200') // -2005) 이 암호화 된 데이터는 어떻게 쓸 수 있나요?
보통 암호화 된 데이터는 클라이언트(브라우저)가 전달받아 다양한 수단(쿠키, 로컬스토리지 등)을 통해 저장하여 API 서버에 요청을 할 때 서버가 요구하는 HTTP 인증 양식에 맞게 보내주어 인증을 시도합니다
비유하자면, 놀이공원의 자유이용권과 비슷합니다.
1. 회원가입: 회원권 구매
- 클라이언트는 회원가입에서 이메일, 패스워드와 같은 정보를 제공합니다.
- 이 정보는 서버에 저장되어, 이후 인증 과정에서 사용됩니다.
2 . 로그인: 회원권으로 놀이공원 입장
- 클라이언트는 이메일, 패스워드로 로그인합니다.
- 서버는 이 정보를 검증한 후, 유효하다면 JWT를 생성하여 클라이언트에게 제공합니다.
3 . 로그인 확인: 놀이기구 탑승 전마다 유효한 회원권인지 확인
- 클라이언트는 로그인 후 모든 API 요청에 JWT를 포함하여 전송합니다.
- 서버는 JWT를 확인하고, 유효하다면 요청된 API를 수행합니다.
4 . 내 정보 조회: 내 회원권이 목에 잘 걸려 있는지 확인하고, 내 이름과 사진, 바코드 확인
- 클라이언트는 JWT를 사용해 자신의 정보를 조회할 수 있습니다.
- 서버는 JWT를 복호화하여 내부에 저장된 정보를 확인하고, 이 정보를 바탕으로 사용자의 세부 정보를 조회하여 전달해줍니다.
'내일배움 강의 > 강의- Node.js 입문, 숙련' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Node.js 숙련주차 4.1 인증(Authentication), 인가(Authorization) - 나만의 게시판 사이트 (1) | 2024.12.02 |
|---|---|
| Node.js 숙련주차 3.7 나만의 게시판 사이트 설계 - DB 테이블 만들기 (0) | 2024.12.02 |
| Node.js 숙련주차 3.5 쿠키(Cookie)와 세션(Session) (1) | 2024.12.01 |
| Node.js 숙련주차 3.3 SQL과 제약 조건(SQL 강의와 겹침) (2) | 2024.11.27 |
| Node.js 숙련주차 3.2 SQL (Structured Query Language) (0) | 2024.11.26 |



